Integrating upstream application to the underlying Kafka system
Metadata can be published into the OneStop system in two different ways, using Registry application REST API or directly integrating upstream applications to the underline OneStop kafka cluster.
This guide will take a look at some approaches for integrating upstream applications and Kafka, and look at some examples regarding the tools Kafka supports.
Before we dive in, it’s worth mentioning the single common data format, Apache Avro, which OneStop application is using for ensuring all data sources and integration points comply to it.
Apache Avro is an open source data serialization format. It relies on schema that define fields and their type. Avro also supports schema evolution. See Avro schema project for details.
Features
Apache NiFi
NiFi is a highly scalable and user friendly UI based system that provides support for data collection and processing. In this case, Nifi can act as a source and sink to bring data to and from Kafka, which helps in automating the flow of data between systems in a Reliable, efficient, and manageable way.
NiFi is able to support multiple versions of the Kafka client in a single NiFi instance. The Apache NiFi 1.10.0 release contains the following Kafka processors:
- ConsumeKafka & PublishKafka using the 0.9 client
- ConsumeKafka_1_0 & PublishKafka_1_0 using the 1.0 client
- ConsumeKafka_2_0 & PublishKafka_2_0 using the 2.0 client
Kafka does not necessarily provide backward compatibility between versions, so use kafka processors that is compatible with the OneStop kafka broker version. See Apache NiFi website page for details.
Nifi as a Producer
A simple use case of NiFi is to act as a Kafka producer, which can bring data from sources directly to a NiFi instance, which can then deliver data to the appropriate Kafka topic. Each instance of PublishKafka could have concurrent tasks executing and each of this tasks publishes messages independently.
Here is the NiFi template with two processors and controller services configuration:
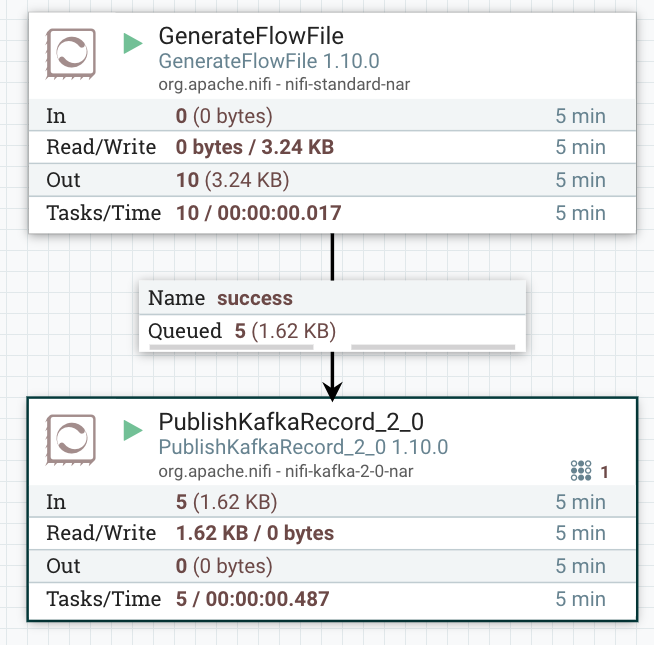
The above example uses GenerateFlowFile processor to create FlowFiles of random data and PublishKafkaRecord processor with the Confluent Schema Registry to publish records to kafka.
Sample Nifi template download the sample nifi template.
Nifi as bidirectional Data Flows
Additional and more complex use case is combining tools such as Kafka, and kafka stream processing platform with Nifi to create a self-adjusting data flow. Kafka Stream is a lightweight library for creating stream processing applications. In this case, NiFi brings data to Kafka which makes it available to a stream processing platform with the results being written back to a different Kafka topic for downstream consumers.
kafka producer
kafka producer uses a Kafka producer API to write a producer that can be used to published record directly to kafka broker. see kafka producer Confluent docs page for details.
Let’s look at a simple Kafka producer implementation using java.
To create a Kafka producer, you need to pass a list of bootstrap servers/Kafka brokers and also specify a client.id that uniquely identifies this Producer client. you will need to specify a Key_serializer and a value_serializer, which Kafka will use to encode the message id as a Kafka record key, and the message body as the Kafka record value.
Import the Kafka packages and define a constant for the producer to connect to the Kafka broker.
import io.confluent.kafka.serializers.AbstractKafkaAvroSerDeConfig;
import io.confluent.kafka.serializers.KafkaAvroSerializer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.Producer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerConfig;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer;
public class KafkaProducerTest {
private final static String TOPIC = "test-topic";
private final static String BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS = "localhost:9092";
private final static String SCHEMA_REGISTRY_URL = "localhost:8081";
private final static String CLIENT_ID = "test-client";
private final static String COMPRESSION_TYPE = "zstd";
private static Producer<Long, String> createProducer() {
props.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS);
props.put(AbstractKafkaAvroSerDeConfig.SCHEMA_REGISTRY_URL_CONFIG, SCHEMA_REGISTRY_URL);
props.put(ProducerConfig.CLIENT_ID_CONFIG, CLIENT_ID);
props.put(ProducerConfig.COMPRESSION_TYPE_CONFIG, COMPRESSION_TYPE);
props.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.name);
props.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, KafkaAvroSerializer.class.name);
return new KafkaProducer<>(props);
}
}
The constant BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG is set to http://localhost:9092 as default which also can be a comma separated list that the Producer uses to establish an initial connection to the Kafka cluster.
The CLIENT_ID_CONFIG value is an id to pass to the server when making requests so the server can track the source of requests.
The KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG value is a Kafka Serializer class for Kafka record keys that implements the Kafka Serializer interface. Notice that we set this to StringSerializer as the message ids type.
The VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG value is a Kafka Serializer class for Kafka record values that implements the Kafka Serializer interface. Notice that we set this to AbstractKafkaAvroSerDeConfig as the message body in OneStop is in Avro format.
Import an Avro schema packages and changing an incoming message to Avro format.
import org.cedar.schemas.avro.psi.Input;
import org.cedar.schemas.avro.psi.Method;
import org.cedar.schemas.avro.psi.OperationType;
import org.cedar.schemas.avro.psi.RecordType;
public class KafkaProducerTest {
...
private static Input buildInputTopicMessage(Map info) {
Input.Builder builder = Input.newBuilder();
builder.setType(RecordType.collection);
builder.setMethod(Method.PUT);
builder.setContent(String.valueOf(info));
builder.setContentType(CONTENT_TYPE);
builder.setSource(SOURCE);
builder.setOperation(OperationType.NO_OP);
return builder.build();
}
}
The builder is setting the require fields which is define here in the Input avro schema definition.
see sample kafka producer java code file for detail.
Kafka connects
Kafka connect, which includes source and sink, can also be used to published data from upstream source into kafka broker. see kafka connect Confluent page for more details.